orld War Two, started wit a clear defined sequence of events, although at the time no one knew what those events would lead to, The war started in China when the Imperial Japanese Army, attacked the Chinese in what has been termed "The Marco Polo Bridge Incident" on July7th 1937. this action sparked the action on the pacific, but it would be more than 2 years when on September 1, 1939 when the German Army proper rolled into Poland starting the World War 2 as the average person knows it.
orld War Two, started wit a clear defined sequence of events, although at the time no one knew what those events would lead to, The war started in China when the Imperial Japanese Army, attacked the Chinese in what has been termed "The Marco Polo Bridge Incident" on July7th 1937. this action sparked the action on the pacific, but it would be more than 2 years when on September 1, 1939 when the German Army proper rolled into Poland starting the World War 2 as the average person knows it.
What follows is a time-line designed to give the visitor a general idea of the most important dates and events during the war years,This is not intended to be a definite time-line by no means there will be some dates and actions missing from it and I'm sure some will consider to be important but were willing to work with the folks to make it as complete as possible, also included will be links to other pages within the site that will explain some of the terms included in the time-line. So kick up your feet and immerse yourself, Six years is a lot of time to cover.
July 7, 1937:
March 11 - 13, 1938:
September 30, 1938:
November 9 - 10, 1938:
March 15 - 16, 1939:
March 31, 1939:
August 23, 1939:
September 1, 1939:
September 3, 1939:
The Marco Polo Bridge Incident marks the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War between China and Japan.
Germany annexes Austria in what is known as the Anschluss, uniting Germany and Austria under Nazi rule.
The Munich Agreement is signed by Germany, Italy, France, & Britain, allowing Germany to annex the Sudetenland, a part of Czechoslovakia with a large ethnic German population. It is made in an attempt to avoid war.
Kristallnacht, also known as the Night of Broken Glass, takes place in Germany and Austria. Nazi paramilitary forces and civilians carry out a widespread attack on Jewish homes, businesses, and synagogues.
German forces occupy the remaining parts of Czechoslovakia, violating the Munich Agreement and effectively annexing the country as the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia.
Italy invades and annexes Albania, expanding its territorial ambitions in the Balkans.
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact is signed between Germany and the Soviet Union, a non-aggression pact between the two countries. The protocols of the pact also divide Eastern Europe into spheres of influence for the two powers.
Germany invades Poland, using blitzkrieg tactics and overwhelming force. This marks the beginning of World War II.
Britain and France declare war on Germany, responding to the invasion of Poland and formally entering the war.
 The Marco Polo Bridge Incident
The Marco Polo Bridge Incident
The Marco Polo Bridge Incident, also known as the Lugou Bridge Incident, occurred on July 7, 1937, near Beijing, China, and marked the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War.
It involved a clash between Chinese and Japanese troops stationed near the Marco Polo Bridge, which spanned the Yongding River.
The incident began when Japanese soldiers, stationed in the area as part of Japan's occupation of Northeast China, conducted a night exercise and claimed that one of their soldiers went missing near the bridge. Demanding permission to conduct a search, they confronted Chinese soldiers guarding the bridge. Tensions escalated, leading to an exchange of gunfire.
The incident quickly escalated into a full-scale battle, with both sides reinforcing their positions and launching attacks. The fighting continued for several days and spread to other areas, resulting in widespread casualties and destruction. The Chinese government under Chiang Kai-shek declared a general mobilization, and the conflict evolved into a full-scale war between China and Japan.
The Marco Polo Bridge Incident was a significant event that intensified the already strained relations between China and Japan. It demonstrated Japan's aggressive expansionist policies and marked a turning point in their military presence in China. The conflict ultimately led to the prolonged and brutal Second Sino-Japanese War, which lasted until Japan's defeat in 1945 and had a profound impact on the region's history.
CLOSE
 The Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement refers to an agreement signed on September 30, 1938, in Munich, Germany, between the leaders of Germany, Italy, France, and Britain. The agreement was intended to resolve the escalating crisis over the Sudetenland, a region of Czechoslovakia with a predominantly German-speaking population.
Adolf Hitler, the German leader, had been pushing for the annexation of the Sudetenland into Germany, claiming it was necessary to protect the rights of ethnic Germans. In response, Czechoslovakia mobilized its military forces, preparing for a potential war with Germany. To avoid a military confrontation, the leaders of Germany, Italy, France, and Britain met in Munich to negotiate a peaceful resolution. The Munich Agreement allowed Germany to annex the Sudetenland, effectively granting Hitler's demands. Czechoslovakia was not invited to participate in the negotiations and was coerced into accepting the terms.
The Munich Agreement was widely criticized as a policy of appeasement, as the Allies sacrificed Czechoslovakia's territorial integrity to avoid conflict with Germany. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain famously declared that the agreement achieved "peace for our time," but it ultimately failed to prevent further aggression by Hitler.
In the months following the Munich Agreement, Germany occupied the rest of Czechoslovakia, and Hitler's expansionist ambitions continued unchecked. The agreement was a stark example of the inability of Western powers to effectively counter Hitler's aggression and demonstrated the limited effectiveness of appeasement policies.
The Munich Agreement is often seen as a symbol of diplomatic failure and a cautionary tale about the dangers of yielding to the demands of aggressive regimes. It is regarded as a significant precursor to the outbreak of World War II, which followed less than a year later with Germany's invasion of Poland
 Kristallnacht
Kristallnacht
Kristallnacht, also known as the Night of Broken Glass, was a pogrom that occurred on the night of November 9-10, 1938, in Nazi Germany. It was a state-sponsored violent attack against Jews, their synagogues, businesses, and homes.
The pretext for Kristallnacht was the assassination of a German diplomat in Paris by a young Jewish refugee. Nazi propaganda used this event as an excuse to incite anti-Jewish sentiment and unleash a wave of violence and destruction.
During Kristallnacht, Nazi paramilitary forces, along with German civilians, targeted Jewish-owned businesses, homes, and synagogues throughout Germany. Jewish individuals were physically assaulted, and countless Jewish-owned properties were vandalized, looted, and set on fire. The streets were filled with shattered glass from broken windows, hence the name "Night of Broken Glass."
The German authorities did little to intervene or prevent the violence. In fact, they actively encouraged and coordinated the attacks. Jewish people were arrested and sent to concentration camps, while their property was confiscated.
Kristallnacht marked a significant escalation in the persecution of Jews in Nazi Germany. It demonstrated the regime's willingness to engage in open violence against the Jewish population and signaled a shift towards a more radical and brutal phase of anti-Semitic policies.
The international response to Kristallnacht varied. While some countries condemned the violence, others remained largely indifferent. The event served as a stark warning about the escalating persecution of Jews in Germany and foreshadowed the horrors of the Holocaust that would unfold in the years to come.
Kristallnacht stands as a dark chapter in history, symbolizing the violent anti-Semitism and systematic oppression unleashed by the Nazi regime. It serves as a reminder of the importance of vigilance against hatred, prejudice, and the grave consequences of state-sanctioned violence targeting a specific religious or ethnic group.
 The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, also known as the Nazi-Soviet Pact, was a non-aggression treaty signed between Germany and the Soviet Union on August 23, 1939, just days before the outbreak of World War II. The pact was named after the foreign ministers of the respective countries at the time: Vyacheslav Molotov of the Soviet Union and Joachim von Ribbentrop of Germany.
The agreement included a public protocol of non-aggression between the two nations, which pledged not to engage in military conflict or support any third party that might attack the other. However, a secret protocol was also signed, dividing Eastern Europe into spheres of influence between the two powers.
The secret protocol of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact outlined the territorial divisions, designating certain countries to fall under either German or Soviet influence. It included the division of Poland, with Germany receiving the western regions and the Soviet Union acquiring the eastern part.
The pact had significant consequences. It provided Hitler with assurances that the Soviet Union would not interfere if Germany invaded Poland, allowing him to launch the war without fear of Soviet intervention. The division of Poland led to the German invasion on September 1, 1939, which marked the beginning of World War II.
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact also allowed the Soviet Union to expand its influence and gain territory in Eastern Europe. In the years following the pact, the Soviet Union occupied and annexed parts of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Finland, and Romania.
The pact was heavily criticized internationally, as it demonstrated the willingness of both Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union to cooperate despite their ideological differences. The agreement shattered the illusion of Soviet opposition to fascism and shocked many countries that had hoped for a united front against Hitler's aggression.
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact remained in effect until June 1941 when Germany violated the agreement and launched a surprise invasion of the Soviet Union. The pact's dissolution led to the Soviet Union joining the Allied forces in their fight against Germany during World War II.
Overall, the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact was a significant diplomatic maneuver that provided a strategic advantage to both Germany and the Soviet Union in the early stages of World War II. However, its secret protocol and the subsequent territorial divisions ultimately set the stage for further aggression and conflict in Eastern Europe.
 The Anschluss
The Anschluss
The Anschluss refers to the annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany on March 12, 1938. The term "Anschluss" means "union" or "connection" in German. Adolf Hitler, the leader of Nazi Germany, aimed to unite Austria with Germany as part of his broader territorial ambitions known as the "Greater German Reich."
Under the pretext of promoting German nationalism and protecting ethnic Germans living in Austria, Hitler pressured the Austrian government into accepting the Anschluss. He utilized both political maneuvering and the threat of military intervention to ensure compliance.
On March 11, 1938, German troops crossed the Austrian border, and the next day, Hitler declared Austria a part of the German Reich. The annexation was met with mixed reactions in Austria. While some Austrians welcomed the union with Germany, others opposed it.
The international response to the Anschluss varied. Although the Treaty of Versailles prohibited the union of Germany and Austria, many countries, including Great Britain and France, offered little resistance. This lack of opposition effectively allowed the Anschluss to proceed without significant consequences.
The Anschluss had profound consequences for both Austria and Germany. Austria lost its independence and became a part of Nazi Germany, subject to the policies and control of the Nazi regime. The annexation also strengthened Hitler's position domestically, boosting his popularity and consolidating his power.
Internationally, the Anschluss heightened concerns about Hitler's expansionist ambitions and his willingness to violate international treaties. It further destabilized Europe and set the stage for subsequent acts of aggression by Nazi Germany, ultimately leading to the outbreak of World War II.
The Anschluss remains a significant event in history, representing a key step in Hitler's quest for territorial expansion and the consolidation of Nazi power in Europe.
April 9, 1940:
May 10, 1940:
May 26 - June 4, 1940:
June 10:, 1940:
June 14, 1940:
July 10, 1940:
September 7, 1940:
October 28, 1940:
November 14, 1940:
December 9, 1940:
Germany launches Operation Weserübung, invading Denmark & Norway to secure important strategic positions and resources. This period is known as the "The Phoney War"
Germany launches a massive invasion of France and the Low Countries, bypassing the heavily fortified Maginot Line. Within weeks, German forces reach the English Channel, trapping British and French troops at Dunkirk.
Operation Dynamo, the evacuation of Allied troops from Dunkirk, takes place. Over 300,000 soldiers are successfully rescued and brought back to Britain.
Italy, under the leadership of Benito Mussolini, declares war on France and Britain, entering the war on Germany's side.
France signs an armistice with Germany, dividing the country into occupied and unoccupied zones. The collaborationist Vichy government is established in the unoccupied zone of France.
The Battle of Britain begins as the German Luftwaffe launches a sustained aerial bombardment of Britain, targeting cities and military installations. The Royal Air Force (RAF) successfully defends the country against the Luftwaffe's attacks, marking a significant turning point in the war.
The London Blitz begins as the German Luftwaffe intensifies its bombing campaign against British cities, focusing on London. The bombings continue throughout the year and into 1941, causing significant damage and casualties.
Italy invades Greece but is eventually repelled by Greek forces with support from the British.
The bombing of Coventry occurs, with the German Luftwaffe launching a devastating air raid on the city of Coventry in England, causing widespread destruction and loss of life.
British forces in North Africa launch Operation Compass, a successful offensive against Italian forces in Libya, resulting in significant gains for the Allies.
These events in 1940 marked significant developments in the early stages of World War II. Germany's Blitzkrieg tactics led to the rapid conquest of France and the Low Countries, while the Battle of Britain showcased the resilience of the British RAF against the German air force. The year also saw Italy entering the war, the establishment of the Vichy government in France, and significant military operations in North Africa.
 The Phoney War
The Phoney War
The Phoney War, also known as the "Sitzkrieg" or "Bore War," was a period of limited military action and relative calm that occurred during the early stages of World War II. It took place from September 1939 to April 1940 and primarily involved the Western Front, where German forces faced off against the Allies.
The Phoney War began with the German invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. France and the United Kingdom, bound by mutual defense agreements with Poland, declared war on Germany but did not launch any major offensives to support their ally. Instead, both sides adopted a strategy of waiting and fortifying their positions, hoping to avoid a repeat of the devastating trench warfare of World War I.
During this period, the conflict was characterized by a lack of significant military engagements. The Western Front, where German forces were stationed, remained relatively quiet. Both sides engaged in limited operations, such as minor skirmishes and occasional artillery exchanges, but no major offensive action was taken.
The Phoney War was marked by a sense of uncertainty and unpreparedness on both sides. The Allies had hoped that the Maginot Line, a complex network of fortifications along the French-German border, would deter any German invasion. Meanwhile, the German High Command focused its attention on planning the invasion of France, rather than launching a full-scale assault during this phase.
As months passed with little action, public sentiment and morale began to wane in both camps. The lack of progress on the battlefield raised questions about the effectiveness of the military strategies employed and the commitment of the Allies to the war effort.
The Phoney War came to an abrupt end in April 1940 when Germany launched its Blitzkrieg invasion of Denmark and Norway. This marked the beginning of a new phase in the war, with swift German advances and the eventual fall of France in 1940.
In hindsight, the Phoney War is seen as a missed opportunity by the Allies to take decisive action against Germany. The period highlighted the need for more coordinated and aggressive strategies to confront the German war machine. Ultimately, the Phoney War served as a prelude to the larger and more intense conflicts that would follow in the subsequent years of World War II.
CLOSE
 The Maginot Line
The Maginot Line
The Maginot Line was a massive system of fortifications constructed by France along its eastern border during the 1930s. Named after French Minister of War André Maginot, the defensive line aimed to deter any potential invasion from Germany and protect the country against a repeat of the devastating trench warfare experienced in World War I.
Construction of the Maginot Line began in the late 1920s and continued into the 1930s. The line stretched from the Swiss border to the Ardennes Forest, covering approximately 940 kilometers (580 miles). It consisted of a complex network of concrete forts, underground bunkers, artillery emplacements, tank traps, and other defensive structures.
The line was designed to force any potential invader, primarily Germany, to funnel their forces through a series of heavily fortified positions. The forts were equipped with state-of-the-art weaponry, including artillery, machine guns, and anti-tank weapons. They were interconnected by a network of underground tunnels and railways for supplies, communication, and troop movements. The Maginot Line was considered an impressive feat of engineering and military planning. It was intended to provide a secure defense against a direct frontal assault, making it difficult for enemy forces to penetrate and bypass the line. The belief was that any attacker would be bogged down and sustain heavy casualties while facing the formidable fortifications.
However, the Maginot Line had some inherent weaknesses. Its construction focused on the eastern border with Germany, neglecting the heavily forested and less fortified Ardennes region in the north. This gap in the line would later be exploited by the German forces during the invasion of France in 1940. Additionally, the Maginot Line was a static defensive system, designed for a traditional war of attrition rather than the fast-paced, mobile warfare employed by the Germans. It did not account for the speed and flexibility of the German Blitzkrieg tactics, which emphasized swift and concentrated armored offensives.
When Germany invaded France in May 1940, they avoided the heavily fortified Maginot Line altogether by advancing through the Ardennes Forest and attacking from the north. The line's defensive capabilities became largely irrelevant as the German forces outmaneuvered and overwhelmed the French defenses from an unexpected direction.
The failure of the Maginot Line demonstrated the limitations of purely defensive strategies and the need for flexibility and adaptability in warfare. It serves as a reminder that a comprehensive defense must consider all potential avenues of attack and be prepared for changing tactics and technology. Despite its ultimate shortcomings, the Maginot Line remains an iconic symbol of military fortification and a testament to the interplay between strategy, technology, and the evolving nature of warfare.
CLOSE
 Operation Dynamo
Operation Dynamo
Operation Dynamo, also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, was a large-scale evacuation carried out by the Allied forces during World War II. It took place between May 26 and June 4, 1940, in the French port city of Dunkirk, where British and French troops were trapped by the advancing German army.
After the German invasion of France, the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and other Allied troops found themselves surrounded and facing imminent capture or annihilation. As the situation grew dire, the decision was made to evacuate the troops by sea.
Operation Dynamo involved a massive rescue effort that mobilized a flotilla of naval vessels, merchant ships, and privately owned boats. Over the course of nine days, these vessels braved heavy German aerial and artillery bombardment to ferry troops from the beaches of Dunkirk to larger ships waiting offshore.
The operation faced numerous challenges, including shallow waters, damaged harbors, and limited resources. However, a combination of careful planning, the dedication of naval personnel, and the bravery of civilian volunteers led to the successful evacuation of over 338,000 Allied troops, including approximately 218,000 British soldiers.
Despite facing constant attacks from the air, the Royal Air Force (RAF) played a crucial role in providing air cover and fending off German aircraft, ensuring the safe passage of the evacuation vessels. This air superiority was instrumental in protecting the ships and minimizing casualties.
Operation Dynamo was a significant turning point in the early stages of the war. Although the Allies had suffered a military defeat in France, the successful evacuation preserved a substantial portion of the BEF and other Allied forces. This allowed them to regroup, rearm, and ultimately contribute to the later Allied victories.
The operation also had important symbolic significance. The determination and resilience displayed by the British people, as well as the cooperation between the military and civilian sectors, boosted morale and demonstrated the resolve to continue the fight against Nazi Germany.
Operation Dynamo stands as a remarkable testament to the power of collective effort, improvisation, and perseverance in the face of overwhelming odds. It remains an iconic event in British and Allied history, symbolizing both the bravery of the troops involved and the indomitable spirit of those who came to their rescue.
CLOSE
 The Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain was a pivotal air campaign fought between the British Royal Air Force (RAF) and the German Luftwaffe during World War II. Lasting from July to October 1940, it was a critical confrontation that aimed to establish German air superiority over Britain and potentially pave the way for a German invasion.
The battle began with Luftwaffe attacks on British coastal targets and shipping, but soon shifted focus to targeting RAF airfields, aircraft, and infrastructure. The RAF, led by Air Chief Marshal Hugh Dowding, employed innovative tactics such as radar-based early warning systems and a flexible command structure to effectively defend against the German onslaught. The Luftwaffe, under the command of Hermann Göring, initially sought to weaken the RAF through aerial bombardment and engage in large-scale dogfights. However, they faced stiff resistance from the RAF's skilled pilots, including the famous Spitfire and Hurricane fighters. The RAF's ability to rapidly repair and replace aircraft played a crucial role in sustaining their defensive efforts.
Throughout the battle, the Luftwaffe intensified its attacks, particularly during the intense period known as the "Blitz." British cities, including London, faced heavy bombing, but the RAF managed to maintain its defense, inflicting significant losses on the Luftwaffe and preventing German air superiority.
The turning point of the Battle of Britain came in September 1940 when the Luftwaffe shifted its focus to targeting London in an attempt to break British morale. This strategic shift allowed the RAF to regroup and recover, leading to a successful defense against German attacks.
Ultimately, the Battle of Britain ended in a decisive victory for the RAF and marked the first significant setback for Nazi Germany in the war. The Luftwaffe's failure to gain air superiority over Britain forced Hitler to postpone his plans for an invasion and turn his attention toward other fronts.
The Battle of Britain had far-reaching consequences. It demonstrated the effectiveness of air defense systems, the importance of radar technology, and the courage and skill of RAF pilots. The victory also served as a morale boost for the British people and provided a turning point in the war, showcasing the resilience and determination of a nation under attack.
The Battle of Britain remains an important event in military history, symbolizing the bravery of those who fought and the importance of air power in modern warfare. It stands as a testament to the strength and resolve of the British people in the face of overwhelming odds and as a crucial moment in the broader struggle against Nazi Germany.
CLOSE
 The London Blitz
The London Blitz
The London Blitz was a sustained and intense bombing campaign carried out by the German Luftwaffe against London and other major cities in Britain during World War II. Lasting from September 1940 to May 1941, the Blitz aimed to break British morale, cripple infrastructure, and pave the way for a German invasion.
The Blitz began on September 7, 1940, with a massive aerial bombardment of London. German bombers targeted residential areas, industrial centers, and key infrastructure, including transportation hubs, docks, and communication networks. The raids were characterized by a relentless wave of bombings, often continuing for consecutive nights.
London bore the brunt of the attacks, enduring heavy bombing for consecutive months. The city's iconic landmarks, such as St. Paul's Cathedral and the Houses of Parliament, were repeatedly targeted. The civilian population faced immense hardships, as homes, schools, hospitals, and businesses were destroyed, and thousands of lives were lost.
The resilience of the British people during the Blitz was remarkable. Despite the devastation and loss of life, Londoners displayed courage and determination, seeking shelter in underground stations, basements, and makeshift air raid shelters. The strength of community spirit and the resolve to withstand the bombings became a symbol of British resistance. The Blitz also highlighted the importance of civil defense and emergency services. The Air Raid Precautions (ARP) and the Home Guard played crucial roles in organizing and protecting the civilian population. Firefighters, medical personnel, and ordinary citizens volunteered to help in rescue and recovery efforts.
Although the Blitz inflicted significant damage and loss of life, it did not break British morale or force the country into surrender. The British Royal Air Force (RAF) successfully defended against Luftwaffe attacks and inflicted heavy losses on German bombers. The Blitz also diverted German attention from strategic targets and military installations, potentially altering the course of the war.
By May 1941, the intensity of the bombing raids decreased as Germany shifted its focus to other fronts. The Blitz had lasting effects on the physical and psychological landscape of Britain, but it failed to achieve its objectives of demoralizing the population or paving the way for invasion.
The London Blitz remains a significant chapter in British history, demonstrating the strength and resilience of the civilian population in the face of relentless enemy attacks. It stands as a testament to the spirit of endurance, unity, and determination displayed by the people of London and other affected cities during a time of immense hardship and danger.
CLOSE
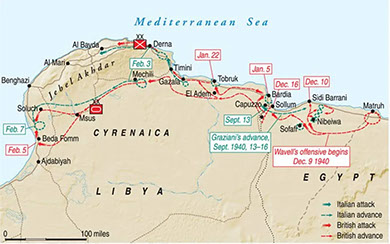 Operation Compass
Operation Compass
Operation Compass was a military campaign conducted by the British Commonwealth forces in North Africa during World War II. It took place from December 1940 to February 1941 and aimed to counter Italian forces in the region and reclaim British-held territories.
The operation began with a series of successful offensives launched by the British Western Desert Force against the Italian forces in Libya. Led by Lieutenant-General Richard O'Connor, the British Commonwealth forces swiftly advanced and pushed back the Italian troops, who were ill-prepared and poorly equipped. Operation Compass utilized a combination of armored warfare and mobile infantry tactics. The British forces employed the use of tanks, particularly the Matilda and Cruiser tank models, which proved superior to the Italian tanks. The British also utilized their advantage in air power to support ground operations.
The Italian forces, under the command of General Rodolfo Graziani, were caught off guard by the swift and aggressive British advances. They lacked proper coordination and effective leadership, which allowed the British forces to encircle and capture tens of thousands of Italian troops.
As the operation progressed, the British Commonwealth forces continued to press their advantage, liberating significant territories and capturing key towns, including Tobruk and Bardia. The success of Operation Compass was a major boost to British morale and showcased the capabilities of the Commonwealth forces in desert warfare.
Operation Compass marked a significant turning point in the North African campaign. It not only inflicted heavy casualties on the Italian forces but also exposed their weaknesses and shattered the myth of Italian military superiority. The operation also secured vital supply lines and set the stage for further British offensives in the region.
Despite its initial successes, Operation Compass did not fully eliminate the Italian threat in North Africa. The campaign was temporarily halted to divert resources to other theaters of the war, allowing the Italians to regroup and receive German reinforcements under the command of General Erwin Rommel. Nevertheless, Operation Compass demonstrated the effectiveness of mobile warfare, showcased the capabilities of the British Commonwealth forces, and set the stage for future Allied successes in North Africa. It served as a stepping stone towards the ultimate expulsion of Axis forces from the region and the eventual Allied victory in the North African campaign.
CLOSE
January 22, 1941:
March 11, 1941:
April 6, 1941:
April 17, 1941:
April 27, 1941:
May 10, 1941:
June 8, 1941:
June 22, 1941:
July 7, 1941:
August 14, 1941:
September 8, 1941:
December 7, 1941:
December 8, 1941:
British and Commonwealth forces in Tobruk, Libya, launch a successful counterattack against the German-Italian Axis forces during the Siege of Tobruk.
President Franklin D. Roosevelt signs the Lend-Lease Act, allowing the United States to provide military aid to Allied countries.
Germany invades Greece and Yugoslavia, quickly overpowering their defenses.
Yugoslavia surrenders to Germany.
Greece surrenders to Germany, ending the Greek campaign.
Germany launches Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union. It becomes the largest military operation in history, marking a major turning point in the war.
British forces in North Africa launch Operation Battleaxe, attempting to relieve the besieged Tobruk. The operation ends in failure.
Germany reaches the outskirts of Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg), beginning the Siege of Leningrad, which lasts until 1944.
United Kingdom and Soviet Union sign a mutual assistance pact, cementing their alliance against Germany.
Atlantic Charter, a joint statement by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, outlines the goals for a post-war world based on democratic principles.
The Siege of Leningrad begins, with German forces encircling the city. The siege lasts for nearly 900 days, resulting in a devastating humanitarian crisis.
Japan launches a surprise attack on the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, leading to the entry of the United States into World War II.
The United States declares war on Japan, followed by declarations of war against the United States by Germany and Italy.
These events in 1941 were significant in shaping the course of World War II. The German invasion of the Soviet Union marked a major shift in the war's Eastern Front. The attacks on Greece, Yugoslavia, and Pearl Harbor expanded the global scope of the conflict. The Siege of Leningrad and the signing of the Atlantic Charter also had long-lasting consequences for the war and the post-war world.

January 1 - 7. 1942:
February 15 - 18, 1942:
April 9-14, 1942:
May 4 - 8, 1942:
June 4 - 7, 1942:
August 7 - 9, 1942:
October 23 - 26, 1942:
November 8, 1942:
November 19 - 23, 1942:
The Battle of Bataan begins in the Philippines as Japanese forces launch a major offensive against American and Filipino troops. The battle lasts for several months before the defenders are overwhelmed and forced to surrender.
The Fall of Singapore occurs as British forces, considered an impregnable fortress, surrender to the Japanese. It is a major blow to Allied morale and marks the largest surrender of British-led forces in history.
The Battle of Bataan ends with the surrender of American and Filipino forces to the Japanese. The captured soldiers are subjected to the infamous Bataan Death March, a brutal forced march to prisoner-of-war camps.
The Battle of the Coral Sea takes place between the United States and Japan in the Pacific. It is the first naval battle fought entirely by carrier-based aircraft and ends in a strategic victory for the Allies.
The Battle of Midway, a decisive naval battle in the Pacific, occurs between the United States and Japan. The U.S. Navy successfully defeats the Japanese fleet, destroying four aircraft carriers and shifting the balance of power in the Pacific theater.
The Battle of Guadalcanal begins with U.S. Marines landing on the island. It marks the start of a long and fierce campaign against Japanese forces in the Pacific and is the first major offensive by Allied forces against Japan.
The Second Battle of El Alamein takes place in Egypt. British forces, under the command of General Bernard Montgomery, decisively defeat German and Italian forces, halting their advance in North Africa.
Operation Torch, the Allied invasion of French North Africa, begins. American and British forces land in Morocco and Algeria, marking the first major offensive against Axis forces in the European theater.
The Battle of Stalingrad intensifies as Soviet forces launch a counteroffensive against German troops. It becomes a major turning point in the war on the Eastern Front, leading to the eventual defeat of the German Sixth Army in early 1943.
These events in 1942 were significant in shaping the course of World War II. The battles in the Pacific demonstrated the increasing strength of the United States against Japan, while the battles in North Africa and the Soviet Union began to turn the tide against the Axis powers. The fall of Singapore and the surrender of Bataan were notable defeats for the Allies, highlighting the challenges they faced. Overall, 1942 was a critical year with major military engagements and strategic shifts in the war.

January 14 - 24. 1943:
January 31, 1943:
May 13 - June 1, 1943:
July 5-28, 1943:
July 10, 1943:
July 25 -
August 17, 1943:
September 8, 1943:
September 9 - 12, 1943:
November 28 -
December 1, 1943:
December 24, 1943:
The Casablanca Conference is held in Morocco, where Allied leaders Churchill and Roosevelt agree on a strategy of unconditional surrender by the Axis powers.
The Battle of Stalingrad concludes as Soviet forces defeat the German Sixth Army, marking a turning point in the war on the Eastern Front.
The Battle of Attu takes place in the Aleutian Islands, with U.S. forces recapturing the island from the Japanese.
The Allied invasion of Sicily, codenamed Operation Husky, starts, leading to the fall of Mussolini and the collapse of Fascist Italy.
Allied forces launch Operation Husky by landing in Sicily, leading to the eventual liberation of the island from Axis control.
The Battle of Kursk, the largest tank battle in history, takes place on the Eastern Front. The Soviet Union successfully repels a major German offensive, turning the tide of the war on the Eastern Front.
The Italian government surrenders to the Allies, marking a significant blow to the Axis powers in Europe.
The Allied invasion of mainland Italy begins, with landings at Salerno and Taranto.
The Tehran Conference is held, bringing together Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin to discuss the strategic direction of the war and post-war plans.
The Cairo Conference takes place, with Churchill, Roosevelt, and Chiang Kai-shek discussing the strategy for defeating Japan and the future of post-war Asia.
These events in 1943 marked significant developments in the war, including Allied victories in North Africa and the Pacific, the successful defense of the Soviet Union against Germany, and the surrender of Italy. The conferences held during this year also shaped the future course of the war and post-war world order.

January 22. 1944:
June 6, 1944:
June 22, 1944:
July 20, 1944:
August 1, 1944:
August 15, 1944:
September 17, 1944:
October 20, 1944:
December 16, 1944:
The Allies launch the Anzio landings in Italy, attempting to bypass German defenses and capture Rome.
June 4: Rome is captured by the Allies, marking the first Axis capital to fall.
D-Day, the Allied invasion of Normandy, France, begins. Over 150,000 troops from the United States, Britain, and Canada land on the beaches of Normandy in the largest amphibious invasion in history.
Operation Bagration, a major Soviet offensive on the Eastern Front, begins. It ultimately results in the destruction of German Army Group Center.
The failed assassination attempt on Adolf Hitler takes place. The plot, known as the July 20 Plot or Operation Valkyrie, seeks to overthrow the Nazi regime.
The Warsaw Uprising begins in Poland, with Polish resistance fighters attempting to liberate the city from German occupation. The uprising lasts for 63 days but is ultimately suppressed by German forces.
Operation Dragoon, the Allied invasion of southern France, commences. It involves landings in Provence and aims to support the D-Day invasion and liberate France.
Operation Market Garden, a massive Allied airborne operation in the Netherlands, is launched. It aims to secure a series of bridges and create a path into Germany but falls short of its objectives.
The Battle of Leyte Gulf, the largest naval battle in history, takes place in the Philippines. The United States defeats the Japanese navy, effectively ending Japan's ability to conduct large-scale naval operations.
The Battle of the Bulge begins as Germany launches a surprise offensive against Allied forces in the Ardennes region of Belgium, hoping to split the Allied lines. The battle lasts until January 1945 and marks the last major German offensive of the war.
These events in 1944 were crucial in the progression of the war. D-Day opened a new front in Europe, the Eastern Front saw significant Soviet advances, and important battles and operations took place in Italy, France, and the Pacific. The failed assassination attempt on Hitler and the Warsaw Uprising demonstrate resistance efforts against the Nazi regime. Overall, 1944 witnessed significant military campaigns and strategic developments that shaped the outcome of World War II.
January 27. 1945:
February 4 - 11, 1945:
February 13-15, 1945:
April 12, 1945:
April 25, 1945:
April 30, 1945:
May 2, 1945:
May 7 - 8, 1945:
July 17 - August 2, 1945:
August 6 and 9, 1945:
August 15, 1945:
September 2, 1945:
Soviet forces liberate Auschwitz concentration camp in Poland, revealing the horrors of the Holocaust.
The Yalta Conference takes place, with leaders from the United States, Soviet Union, and United Kingdom discussing the post-war reorganization of Europe.
The bombing of Dresden occurs, resulting in a devastating firestorm and significant loss of life.
U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt dies; Vice President Harry S. Truman assumes the presidency.
American and Soviet forces meet at the Elbe River in Germany, effectively dividing the country.
Adolf Hitler commits suicide in his bunker in Berlin.
Berlin falls to the Soviet Union, marking the end of the Battle of Berlin and the complete collapse of Nazi Germany.
Germany surrenders unconditionally to the Allies, officially ending the war in Europe. This day is known as Victory in Europe (V-E) Day.
The Potsdam Conference is held, bringing together the leaders of the Soviet Union, United States, and United Kingdom to discuss the administration of post-war Germany and other important issues.
The United States drops atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, leading to Japan's surrender.
Emperor Hirohito of Japan announces Japan's surrender, bringing an end to World War II. This day is known as Victory over Japan (V-J) Day.
The formal surrender ceremony takes place aboard the USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay, officially marking the end of World War II.
These events in 1945 marked significant turning points and the ultimate conclusion of the war, both in Europe and the Pacific. The year saw the demise of Hitler and the Nazi regime, the use of atomic weapons, and the final surrender of Japan, bringing about a new era in world history.

October 24, 1945:
June 5, 1947:
August 15, 1947:
December 10, 1947:
April 4, 1948:
May 14, 1948:
June 24, 1948:
April 4, 1949:
August 29, 1949:
October 1, 1949:
The United Nations is officially established, It's goal of promoting peace, international cooperation, and the prevention of future conflicts.
The Marshall Plan is announced by U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall. It aims to provide economic assistance to war-torn European countries in order to rebuild and prevent the spread of communism.
India gains independence from British rule, leading to the partition of India and the creation of the separate nations of India and Pakistan.
The United Nations General Assembly adopts the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, establishing a set of fundamental human rights and principles.
The North Atlantic Treaty is signed, establishing the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) as a military alliance between North American and European countries to counter potential aggression from the Soviet Union.
The State of Israel is established, leading to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict in the Middle East.
The Berlin Blockade begins as the Soviet Union blockades West Berlin, leading to the Berlin Airlift by the United States and its allies to provide essential supplies to the city.
The North Atlantic Treaty comes into effect, officially establishing NATO as a defensive alliance.
The Soviet Union successfully tests its first atomic bomb, escalating the arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union.
The People's Republic of China is proclaimed by Mao Zedong, following the victory of the Chinese Communist Party in the Chinese Civil War.
These events in the years after World War II set the stage for the Cold War, shaped the geopolitical landscape, and laid the foundation for the post-war era. The establishment of the United Nations, the creation of NATO, and the emergence of new nations demonstrated the efforts to promote international cooperation and maintain global stability. The division of India, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, and the escalation of the arms race were among the enduring consequences of the post-war period.






ALL MATERIAL PRODUCED FOR THIS SITE © COPYRIGHT 2023 - 2024 STUDIOBIRD